Chapter Overview
This chapter introduces the cell as the fundamental unit of life. It explains the structure and functions of cells, covering key organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and more. The chapter also highlights the differences between plant and animal cells, and discusses the significance of cells in overall life processes.
Important Keywords
- Cell: The basic unit of life.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell containing genetic material.
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like substance in which cell organelles are suspended.
- Cell Membrane: The semi-permeable membrane that regulates what enters and exits the cell.
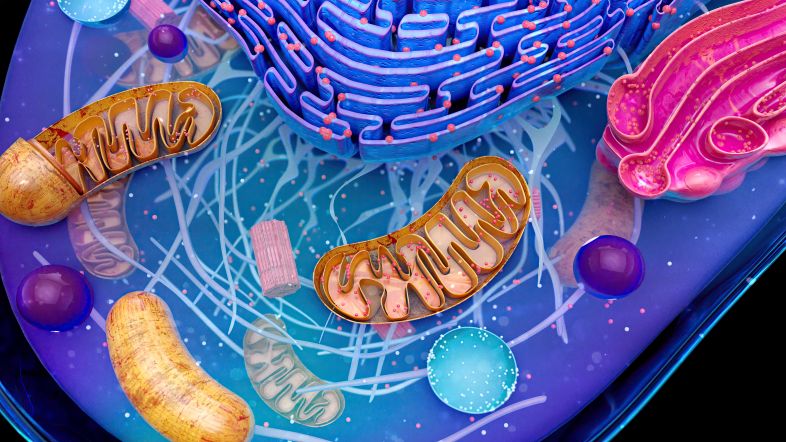
- Mitochondria: Organelles that generate energy through respiration.
- Chloroplast: Organelles found in plant cells that conduct photosynthesis.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: The organelle responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins.
- Lysosome: An organelle containing enzymes for digestion and waste removal.
- Ribosome: The site of protein synthesis.
- Eukaryotic: Cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic: Cells without a nucleus, typically smaller and simpler.
